Agile and scrum working
Aug 22, 2024
How did we get here?
- Waterfall approaches were used in the early days of software development
- Requirements; Design; Development; Integration; Testing; Deployment
- You only move to the next stage when the first one is complete
- (although actually it turns out you kind of don’t…)
The road to agile
- Some of the ideas for agile floated around in the 20th century
- Shewart’s Plan-Do-Study-Act cycle
- The New New Product Development Game in 1986
- Scrum (which we’ll return to) was proposed in 1993
- In 2001 the Manifesto for Agile Software Development was published
The agile manifesto

Copyright © 2001 Kent Beck, Mike Beedle, Arie van Bennekum, Alistair Cockburn, Ward Cunningham, Martin Fowler, James Grenning, Jim Highsmith, Andrew Hunt, Ron Jeffries, Jon Kern, Brian Marick
Robert C. Martin, Steve Mellor, Ken Schwaber, Jeff Sutherland, Dave Thomas
this declaration may be freely copied in any form, but only in its entirety through this notice.
Agile principles- software and the MVP
- Our highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software.
- Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference to the shorter timescale.
- Working software is the primary measure of progress.
(these principles and those on following slides copyright Ibid.)
Agile principles- working with customers
- Welcome changing requirements, even late in development. Agile processes harness change for the customer’s competitive advantage.
- Business people and developers must work together daily throughout the project.
Agile principles- teamwork
- Build projects around motivated individuals. Give them the environment and support they need, and trust them to get the job done.
- The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation.
- The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams.
- At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly.
Agile principles- project management
- Agile processes promote sustainable development. The sponsors, developers, and users should be able to maintain a constant pace indefinitely.
- Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design enhances agility.
- Simplicity–the art of maximizing the amount of work not done–is essential.
The agile advantage
- Better use of fixed resources to deliver an unknown outcome, rather than unknown resources to deliver a fixed outcome
- Continuous delivery
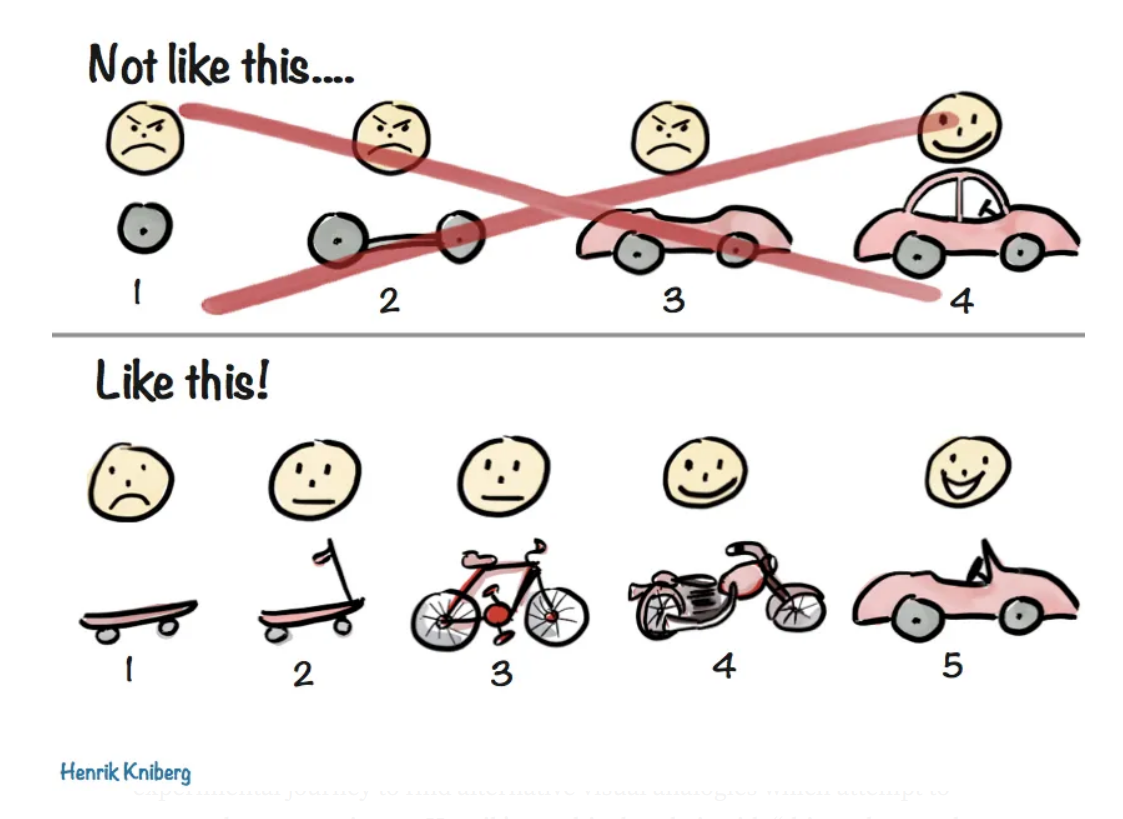
Feature creep
- Users ask for: everything they need, everything they think they may need, everything they want, everything they think they may want
“every program attempts to expand until it can read mail. Those programs which cannot so expand are replaced by ones which can”
Regular stakeholder feedback
- Agile teams are very responsive to product feedback
- The project we’re curently working on is very agile whether we like it or not
- Our customers never know what they want until we show them something they don’t want
More agile advantages
- Early and cheap failure
- Continuous testing and QA
- Reduction in unproductive work
- Team can improve regularly, not just the product
Agile methods
- There are lots of agile methodologies
- I’m not going to embarrass myself by pretending to understand them
- Examples include Lean, Crystal, and Extreme Programming
Scrum
- Scrum is the agile methodology we have adopted
- Despite dire warnings to the contrary we have not adopted it wholesale but most of its principles
- The fundamental organising principle of work in scrum is a sprint lasting 1-4 weeks
- Each sprint finishes with a defined and useful piece of software that can be shown to/ used by customers
Product owner
- This person is responsible for the backlog- what goes in to the sprint
- The backlog should be inclusive of all of the things that customers want or might want
- The backlog should be prioritised
- The product owner does this through deep and frequent conversations with customers
Scrum master helps the scrum team
- “By coaching the team members in self-management and cross-functionality
- Focus on creating high-value Increments that meet the Definition of Done
- Influence the removal of impediments to the Scrum Team’s progress
- Ensure that all Scrum events take place and are positive, productive, and kept within the timebox.”
The backlog
- Having an accurate and well prioritised backlog is key
- Don’t estimate the backlog in hours- use “T shirt sizes” or “points”
- People are terrible at estimating how long things take- particularly in software
- Everything in the backlog needs a defined “Done” state
Sprint planning
- The team, the product owner, and the scrum master plan the sprint
- Sprints should be a fixed length of time less than one month
- The sprint cannot be changed or added to (we break this rule)
- The team works autonomously in the sprint- nobody decides who does what except the team
- Can take three hours and should if it needs to
Standup
- Every day, for no more than 15 minutes (teams often stand up to reinforce this rule) team and scrum master meet
- Each person answers three questions
- What did you do yesterday to help the team finish the sprint?
- What will you do today to help the team finish the sprint?
- Is there an obstacle blocking you or the team from achieveing the sprint goal
Sprint retro
- What went well, what could have gone better, and what to improve next time
- Looking at process, not blaming individuals
- Requires maturity and trust to bring up issues, and to respond to them in a constructive way
- Should agree at the end on one process improvement which goes in the next sprint
- We’ve had some really, really good retros and I think it’s a really important process for a team
Team perspective
- Product owner- that’s me
- Focus, clarity and transparency, team delivery, clear and appropriate responsibilities
- Scrum master- YiWen
- Team member- Matt
- Team member- Rhian
Scrum values
- Courage
- Focus
- Commitment
- Respect
- Openness
Using agile outside of software
- Data science is outside of software (IMHO)
- We don’t have daily standups and some of our processes run longer than in software development
- You can build cars with Agile
- Marketing and UX design
view slides at the-strategy-unit.github.io/data_science/presentations